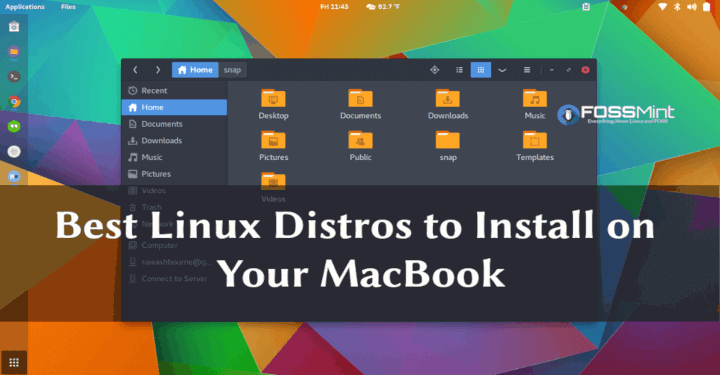
The following article is a guide to installing Linux on a Mac PC. Most of the time we opt for Linux operating systems but are confused about the hardware requirements. The tutorial will help you run Linux system on your Mac which will completely replace the original OS. Read on below to find out:
Every Linux I booted on my MacBook didn't support keyboard, trackpad or Wifi. I connected a keyboard and mouse via USB, but that was still quite useless because then the WiFi still doesn't work. So shortly: I need to know if there is a Linux distribution which supports keyboard, trackpad and wifi of the MacBooks of 2019. Im considering and lilkely will if it works out, purchasing a older Core2 Duo based 15.2' Macbook Pro, I prefer to run Linux on my Laptops (Windows for Gaming but only on my AMD/Nvidia gaming desktop) and was curious as to if anyone would know if I need that Apple bootcamp crap to install it or if I could simply singleboot it as the sole OS.
Before you begin, you’ll first need to select the distribution you want to work on. Whichever you choose will determine the kind of working environment you want. Some of them include:
- Ubuntu: One of the most popular operating systems built on Unity. It is great for new users and offers a very similar environment as macOS does.
- LinuxMint: Released in 2006, this type is more Window- like and comes in with a range of desktops (Cinnamon, Mate etc.) for Users.
- Debian: This is perfect for people working on the server side. Although, Debian is a little complicated to set up and use, but offers a lot more features than Ubuntu and Mint.
- Fedora Linux: This distro is based on various packages such as DNF, RPM and GNOME. It is not recommended for beginners because of the complex working environment.
Try to get familiar with the distribution you want to install so you don’t have any issues later. We recommend starting with Ubuntu since it is the most used and offers plenty of community support in case if you get stuck somewhere.
Installing Linux on a Mac
Yes, there is an option to run Linux temporarily on a Mac through the virtual box but if you’re looking for a permanent solution, you might want to completely replace the present operating system with a Linux distro.
To install Linux on a Mac, you’ll need a formatted USB drive with storage up to 8GB. Remember this process will wipe out your current macOS/OS X installation and there is probably a very hard chance to recover it back. Also, don’t try to run macOS and Linux on dual boot because that won’t work too.
Follow the steps for installation below:
- Download Ubuntu or any other Linux distro you want to the Mac. Save it in your Downloads folder.
- Now download and install Etcher, an app that will help copy the Linux installation file to your USB drive. (https://www.balena.io/etcher/)
- Open the app and click on the Settings icon. Tick on the Unsafe Mode and click on Yes, Continue.
- Now Click on SelectImage. Choose the name of the .iso file you downloaded in Step 1.
- Insert your USB Drive
- Under the SelectDrive option, Click Change. Pick the drive option that matches with your USB drive in size. If you have inserted one drive in your Mac, the option will show /dev/disk1. If there are two drives attached, there will be an option for /dev/disk2 and so on. Note that /dev/disk0 is your Mac’s hard drive. Do not select that option.
- Now click Flash to start copying.
- Remove the USB Flash Drive and Shut down your Mac.
- Now attach the USB drive on the Mac again or to any other PC you want to install it to.
- Power up the PC while constantly holding the Option key
- From the start up screen, select the EFI Boot Option
- You will see a screen with Ubuntu Installation Options that will ask you to either Try Ubuntu or Install Ubuntu. Press the letter ‘e’ to go the boot entry.
- Here, you will have to edit the boot entry. Change the line starting with Linux and add the word ‘nomodeset’ after ‘quiet splash’. It should be like this:
- Now, Press F10
- Ubuntu will start booting into trial mode
- Click on the option, ‘Install Ubuntu’
- Select your Language and Continue
- Now, select the option ‘Install this third party software’ and click continue
- Click Yes to the alert option for /dev/sdb
- Now select ‘Erase Disk and Install Ubuntu’ and click on continue
- Make sure you select the main hard drive and click on Install Now.
- Select your location and then click on continue
- Choose your keyboard layout and click on Continue
- Add a name and Password that you want to use
- Click on Continue and your Linux Distro will start installing
- Once the installation is finished, you will be asked to restart your Mac
- Now, login with your name and password to start using Ubuntu.
Note: During the installation process, we used the entire hard disk for Ubuntu in step 20, which means your MacOS will be permanently deleted. If you want to keep the MacOS, you will have to make disk partitions, a small 8GB partition and a larger 1000GB for Linux. You can also go to Disk Utility to create proper partitions before you start installing Linux. Have a look here (https://linuxnewbieguide.org/how-to-install-linux-on-a-macintosh-computer/)
Last updated on 26 April 2021.
Intro
This article describes how to install Ubuntu Linux on your MacBookPro.
The old version of article can be found here https://nixaid.com/linux-on-macbookpro-old/ (for Ubuntu 18.04).
Hardware
Apple MacBook Pro 'Core i7 2.9 15' Touch/Mid-2017 with AMD Radeon Pro 560
Target Kernel/Distro
Linux >=5.0 on Ubuntu 20.04
Not working but can be worked around
- Audio input & output
Use bluetooth headphones/speakers for audio as a workaround.
If you just want the ISO and skip all the hard work, you can get it here:
Download 3.7G: https://files.nixaid.com/ubuntu4mac.iso
SHA256: 8262d84f54dc1f62bae3f46507e461cc0b4980ba261ac8dad52b8a3ec2eb9a31
Preparing the disk
Partition for your Linux installation
You would need at least 25 GB free disk space for the Ubuntu 20.04 installation.
Reduce your Macintosh HD partition from macOS by using Disk Utility.
The freed space will be used by the Ubuntu Linux installer.
Remastering Ubuntu distro
I used another laptop running Ubuntu to apply the steps described in this section.
There are few drivers and firmware which you need to add to your Linux in order to avoid the unnecessary hassle with connecting external USB keyboard/mouse/stick as most of the howto's suggest.
apple-ib-tb, apple-ibridge, applespi (for the Touchbar, Touchpad, Keyboard) and brcm firmware (for MBP WiFi adapter).
By creating your own remastered Live Ubuntu Linux distribution, you will also have a handy recovery tool you can use at any time.
Get Ubuntu
Download it from its official website https://www.ubuntu.com/download/desktop
Extract the image
Extract the Ubuntu image before you can start remastering it.
Chroot to the image
Once the image is extracted, you will need to continue remastering it from inside. To do so, you will need to use chroot.
Update the image
It is a good idea to keep the software updated.
DKMS: Keyboard, touchpad and touchbar
To avoid hassle with plugging the external keyboard/mouse, you can already build in the keyboard, touchpad and touchbar drivers.
If you want the F-keys to be always on by default and the Fn button for switching from F-keys to special keys, then use the following command:
You can also swap fn and a control keys:
Or remap it to any other key:
Touchpad configuration
Next, you need to set the proper dpi for the touchpad:
Module: USB WiFi TP-LINK TL-WN722N
(OPTIONAL): You can skip this section! There is a way to get your MBP's wifi adapter working, so you do not need the USB WiFi TP-LINK dongle. See the next section Enable MBP's WiFi adapter.
TP-Link TL-WN722N v2 support has been added to the Linux kernel starting v4.13-rc2 https://github.com/torvalds/linux/commit/5a1d4c5dd4eb2f1f8a9b30e61762f3b3b564df70
So you can skip this section entirely if you happened to be using a recent kernel.
In order to enable the external TP-LINK TL-WN722N USB WiFi adapter, you need to make sure the Ubuntu image has the necessary driver.
Enable MBP's WiFi adapter
MBP's Broadcom wifi adapter working in Linux!
All that needs to be done is placing the right brcmfmac43602-pcie.txt file into a /lib/firmware/brcm/ directory.
Get brcmfmac43602-pcie.txt from https://bugzilla.kernel.org/show_bug.cgi?id=193121#c74(should it disappear one day, let me know, I'll share / re-upload it)
Make sure it gets to the initramfs:
Exit chroot environment
Exit the chroot environment when you are done modifying the Ubuntu image.
Update the kernel
To ensure the remastered Ubuntu boots the latest Linux kernel which you have installed in the chrooted system.
Build remastered Ubuntu image
The following steps are to build the remastered Ubuntu image.
When running xorriso, keep in mind the order of arguments is important.
Test the new image
Make sure your remastered image boots, before writing the it to your USB stick.
Out of the following methods, you would likely only need UEFI -> USB.
Install the UEFI firmware and qemu for running virtual machines:
Legacy (BIOS)
CDROM:qemu-system-x86_64 -enable-kvm -m 1G -k en-us -cdrom ubuntu4mac.iso
USB:qemu-system-x86_64 -enable-kvm -m 1G -k en-us -device nec-usb-xhci,id=xhci -drive if=none,id=stick,file=ubuntu4mac.iso,format=raw -device usb-storage,bus=xhci.0,drive=stick
UEFI
CDROM:qemu-system-x86_64 -enable-kvm -m 1G -k en-us -bios /usr/share/ovmf/OVMF.fd -cdrom ubuntu4mac.iso
USB:qemu-system-x86_64 -enable-kvm -m 1G -k en-us -bios /usr/share/ovmf/OVMF.fd -device nec-usb-xhci,id=xhci -drive if=none,id=stick,file=ubuntu4mac.iso,format=raw -device usb-storage,bus=xhci.0,drive=stick
Installing the Linux
Boot your MacBookPro from your newly remastered Ubuntu - ubuntu4mac.iso and create partitions you are going to be installing it to.
Install as normal.
All the modifications which were done to the remastered ISO before will be applied to your installation!
Extra hints
Swap command and option keys
Once you have logged-in under your user in the Gnome/Unity session, run the following command to permanently swap command and option keys:
Windows in QEMU/KVM
You can download Windows 10 for free and install/use it in QEMU/KVM.
https://www.microsoft.com/software-download/windows10
Best Linux For Macbook Pro Mid 2009
Steam in Docker
As a great surprise for some, you can play games in Linux on your MacBookPro using AMD Radeon Pro 560.
For that you can either install Steam on your own or use my Steam image which is much simpler https://hub.docker.com/r/andrey01/steam/
Grub to show options
This is important as one day you may get a Linux kernel that won't boot due to some problem. To prevent this, make sure you are able to choose the kernel when your MBP starts.
To do this, remove the GRUB_HIDDEN_TIMEOUT* lines from the /etc/default/grub file and make sure GRUB_TIMEOUT is set to some reasonable value, e.g. 5 (without quotes).
Then regenerate grub config by running sudo grub-mkconfig -o /boot/grub/grub.cfg command.
This will allow you to see the grub loader options on boot and let you pick a different kernel in case if the last one was having troubles to boot/or any other troubles.
Grub to show macOS High Sierra option
Add the following code to /etc/grub.d/40_custom file:
Then regenerate grub config by running sudo grub-mkconfig -o /boot/grub/grub.cfg command.
After that you do not need to hold the 'option' button to load macOS when restarting your MBP.
When upgrading a Linux kernel
Make sure your kernel drivers have been compiled each time you are getting a Linux kernel upgrade. For that, run dkms status command and see whether the module has installed status there.
Might need to repeat the steps in Module: USB WiFi TP-LINK TL-WN722N.
Troubleshooting
macOS got an update and GRUB is not booting anymore
One day you may find yourself in a situation when only macOS is booting, while GRUB boot loader is being completely skipped.
Do not worry, you can set your Linux boot option back from macOS itself.
You can do this by using the bootoption tool
- Install Xcode from the App Store.
- Install bootoption:
- List your UEFI boot preferences:
You can also see more info for each option:
- Set ubuntu to be 1st in your boot order:
If you get this error, do not worry, this is due to the SIP (System Integrity Protection). All you need is just to disable it (you can enable it later):
After that the commands will work as expected:

Best Linux For Macbook Pro 2008
You can also use sudo bootoption set --bootnext 0000 command for one-time boot.References
- Ubuntu 18.04 Linux on mid-2017 MacBookPro
- Linux On MBP Late 2016
- MBP 2016 Linux
Best Osx For Macbook Pro
Donate me
If you found this useful, please consider making a donation!
Donations
crypto3$paystring.crypto.com- BTC:
bc1qvelutkakstymn244km9kgdd80kdyqnx3wahjcv
Best Linux Distro For Macbook Pro 2015
Alternative ways to make a donation are in the About section https://nixaid.com/about/